Base API Client
Access to many of our data sources happens via similar REST APIs (e.g. SmartSensor API, CMD API). Therefore, a lot of client-code needed for communicating with them is similar and can be reused.
That was the motivation to create a BaseAPIClient class that would be a starting point for
custom API clients we use in our projects.
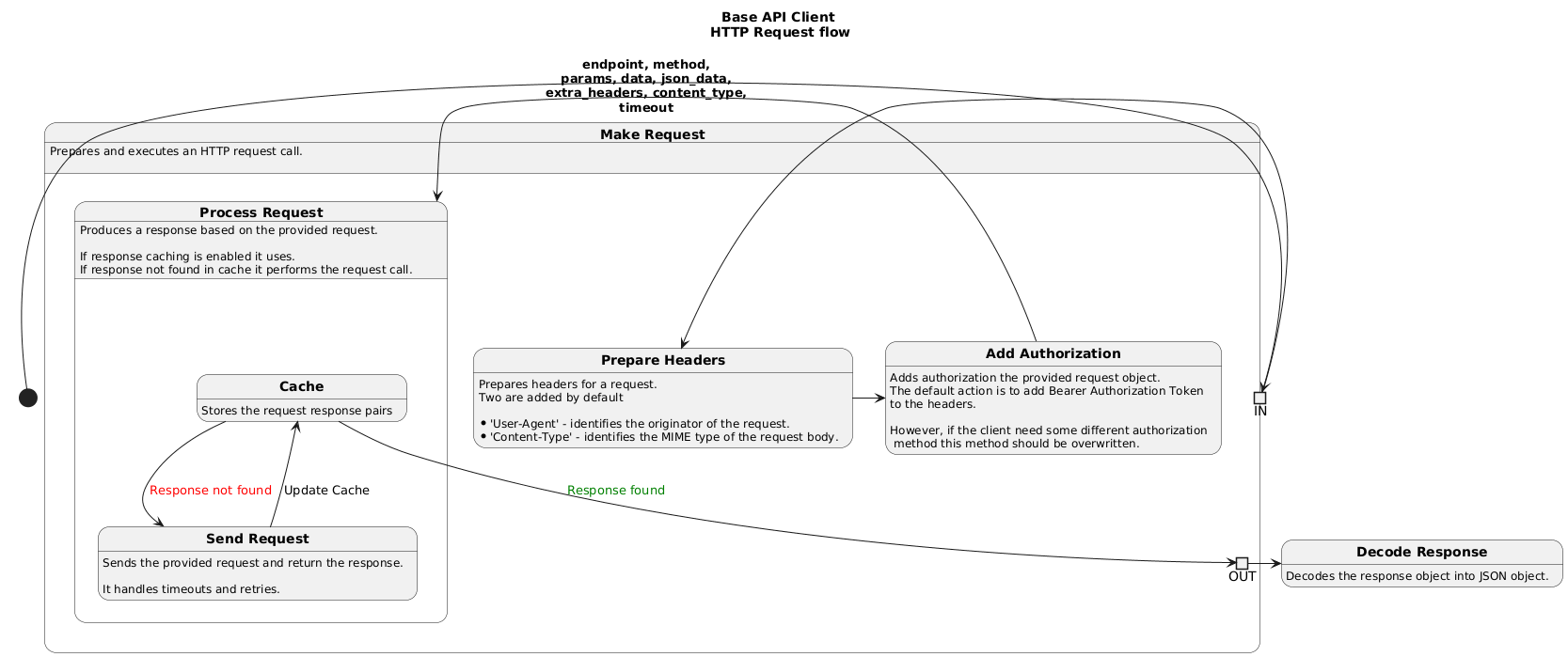
It would handle common activities like authorization, request sending, response parsing, caching once,
and allow the specific API clients to focus on what is unique for them: modeling queries for required
API endpoints.
In this document you will find an overview of BaseAPIClient class, information about what is already implemented,
what has to be implemented for a specific API client implementation and what can be extended or overridden to change
the default behaviour.
Finally, you will find an example on how to build your own API Client based on the BaseAPIClient class.
Components
Full developer API can be found here: BaseAPIClient API
Request Flow
Example
In this example we will build a specific API Client that connects with an imaginary REST API ai-predict.abb.com that
provides an AI models for ABB assets.
This imaginary API has the following requirements:
- Authentication is done by sending the POST Request with
{"mode": "api_key", "api_key": <API_KEY>}json body to the/Authendpoint. - Authorization of the subsequent requests is done by adding a custom header
AbbAuthentication: Bearer <token> - There should be two variants of the client available, standard and expert. To enable expert variant
each request should have one additional header:
ExpertMode: yes
Also, we would need to implement two methods:
get_predictions- calls/Predictionsendpoint with GET method andasset_idparameter.set_model- calls/Modelsendpoint with POST method andasset_id,model_name, andmodel_dataparameters in body.
First steps
We start from creating a new python file in reportconnectors/api_client. Let's call it ai_predict_api_client.py
We will store all of our code there.
Then we can create a new class, that inherit from BaseAPIClient
from reportconnectors.api_client.base_api_client.base_api_client import BaseAPIClient
class AIPredictAPIClient(BaseAPIClient):
"""
Implements an API Client for `ai-predict.abb.com` API.
"""
Because we want to support the Expert mode (third requirement) API variant,
we will extend the standard __init__ method by accepting one extra argument: extra_mode
def __init__(self, url: str, expert_mode: bool = False, **kwargs):
super().__init__(url=url, **kwargs)
self.expert_mode = "yes" if expert_mode else "no"
Authentication & Authorization
Each implementation of API client requires from developer creating a custom version of authenticate method.
We will implement a first requirement: Authentication is done by sending the POST Request
with {"mode": "api_key", "api_key": <API_KEY>} json body to the /Auth endpoint.
from http import HTTPStatus
def authenticate(self, api_key: str) -> bool:
endpoint = "/Auth"
data = {"mode": "api_key", "api_key": api_key}
response = self._make_request(method="POST", endpoint=endpoint, json_data=data)
status_code, decoded_response = self._decode_response(response=response, default={})
abb_access_code = decoded_response.get("abb_access_token", None)
_is_authenticated = (status_code == HTTPStatus.OK) and abb_access_code
if not _is_authenticated:
self.auth_data[self.KeyNames.ACCESS_TOKEN] = abb_access_code
return _is_authenticated
Then we will override a _add_authorization_to_request to override the default authorization logic
to fulfill the second requirement: Authorization of the subsequent requests is done by adding
a custom header AbbAuthentication: Bearer <token>
import requests
def _add_authorization_to_request(self, request: requests.Request) -> requests.Request:
if self.auth_token:
request.headers.update({"AbbAuthentication": f"Bearer {self.auth_token}"})
return request
Automatic token refresh
If you want to implement automatic token refresh, you can override the _make_access_token_refresh(force: bool) method.
It should do all the work needed to refresh the token and return a boolean value that indicates
if the token was successfully refreshed.
When this method is present, and the auto_refresh parameter is set to True,
then the BaseAPIClient will automatically call this method before each request.
It means, that the _make_access_token_refresh(force: bool) should incorporate its own logic to decide if the
token refresh is needed or not. And when the force parameter is set to True, it should always refresh the token.
Additionally, if the response for any request is 401, the BaseAPIClient will automatically call this method
with the force parameter set to True, and then it will repeat the request.
def _make_access_token_refresh(self, force: bool) -> bool:
if self.token_expired or force:
new_token = self.custom_refresh_token_function()
self.set_token(new_token)
return True
return False
Client-specific methods
Finally, we can implement the required public methods.
get_predictions should returned a list of predictions for provided asset_id, and set_model should update
a model with model_data for provided asset_id and model_name
from typing import List, Dict
from http import HTTPStatus
def get_predictions(self, asset_id: str) -> List:
"""
Gets predictions from GET `/Predictions` endpoint using provided `asset_id`
"""
endpoint = "/Predictions"
params = {"asset_id": asset_id}
extra_headers = {"ExpertMode": self.expert_mode}
response = self._make_request(method="POST", endpoint=endpoint, params=params, extra_headers=extra_headers)
decoded_response = self._decode_response(response=response, default={})
return decoded_response
def set_model(self, asset_id: str, model_name: str, model_data: Dict) -> bool:
"""
Sets model using POST `/Predictions` endpoint
"""
endpoint = "/Models"
data = {"asset_id": asset_id, "model_name": model_name, "model_data": model_data}
extra_headers = {"ExpertMode": self.expert_mode}
response = self._make_request(method="POST", endpoint=endpoint, json_data=data, extra_headers=extra_headers)
decoded_response = self._decode_response(response=response, default={})
status_code = self._get_status_code(response=response)
_is_successful = status_code is HTTPStatus.OK and decoded_response.get("status", "") == "success"
return _is_successful
Full example code
from http import HTTPStatus
import requests
from typing import List, Dict
from reportconnectors.api_client.base_api_client.base_api_client import BaseAPIClient
class AIPredictAPIClient(BaseAPIClient):
"""
Implements an API Client for `ai-predict.abb.com` API.
"""
def __init__(self, url: str, expert_mode: bool = False, **kwargs):
# Call base class __init__
super().__init__(url=url, **kwargs)
self.expert_mode = "yes" if expert_mode else "no"
def authenticate(self, api_key: str = None) -> bool:
"""
Authenticates to the API using `/Auth` endpoint and API KEY parameter.
Returns:
True if the client is successfully authenticated. Otherwise, it returns False.
"""
endpoint = "/Auth"
data = {"mode": "api_key", "api_key": api_key}
response = self._make_request(method="POST", endpoint=endpoint, json_data=data)
# We expected JSON object that contains an 'abb_access_token' key with access token that we will later use with
# each subsequent request.
# We consider the Authentication process successful when the status_code is 200 and 'abb_access_code' is present
# and not empty
status_code, decoded_response = self._decode_response(
response=response, default={}
)
abb_access_code = decoded_response.get("abb_access_token", None)
_is_authenticated = (status_code is HTTPStatus.OK) and abb_access_code
if not _is_authenticated:
self.auth_data[self.KeyNames.ACCESS_TOKEN] = abb_access_code
return _is_authenticated
@property
def is_logged(self):
return self.auth_data.get(self.KeyNames.ACCESS_TOKEN) is not None
def _add_authorization_to_request(
self, request: requests.Request
) -> requests.Request:
"""
Adds custom authorization logic to each request:
Add a `AbbAuthentication` header with `Bearer <auth_token>` value
Returns:
Updated request
"""
# self.auth_token is a shortcut to self.auth_data.get(self.KeyNames.ACCESS_TOKEN, None)
if self.auth_token:
request.headers.update({"AbbAuthentication": f"Bearer {self.auth_token}"})
return request
def get_predictions(self, asset_id: str) -> List:
"""
Gets predictions from GET `/Predictions` endpoint using provided `asset_id`
Returns:
List of predictions for a given asset id. If nothing is found, then the empty list is returned.
"""
endpoint = "/Predictions"
params = {"asset_id": asset_id}
extra_headers = {"ExpertMode": self.expert_mode}
response = self._make_request(
method="POST", endpoint=endpoint, params=params, extra_headers=extra_headers
)
decoded_response = self._decode_response(response=response, default=[])
return decoded_response
def set_model(self, asset_id: str, model_name: str, model_data: Dict) -> bool:
"""
Sets model using POST `/Predictions` endpoint
Returns:
True if model is successfully updated, false otherwise.
"""
endpoint = "/Models"
data = {
"asset_id": asset_id,
"model_name": model_name,
"model_data": model_data,
}
extra_headers = {"ExpertMode": self.expert_mode}
response = self._make_request(
method="POST",
endpoint=endpoint,
json_data=data,
extra_headers=extra_headers,
)
decoded_response = self._decode_response(response=response, default={})
status_code = self._get_status_code(response=response)
_is_successful = (
status_code is HTTPStatus.OK
and decoded_response.get("status", "") == "success"
)
return _is_successful